A vacuum pump is a device that creates a partial vacuum or full vacuum by removing or eliminating gas from an enclosed, sealed space. Note that the vacuum pump is not the same thing as an air compressor, which increases gas by reducing its volume. Read More…
Busch Vacuum Solutions is a leading manufacturer of vacuum pumps, blowers, compressors, and customized systems using vacuum technology. With over 60 years of experience, Busch offers the largest selection of industrial vacuum and pressure technology available today to meet their customer’s operating and cost saving goals. Contact us today!
Founded in 1885, Becker is still family owned and a leader in innovation. From their innovative products & designs to their team of loyal, experienced & talented employees, you will find the solutions you are looking for at Becker. Becker’s vacuum pumps are of the highest quality and you are guaranteed to go home satisfied and continue to be satisfied in the many years to come.
Gast Manufacturing specializes in rotary vane, oilless, miniature, high-volume and dry vacuum pump products. We provide efficient, reliable vacuum pumps for a variety of applications. Our commitment to quality products, great service and environmentally friendly practices is unparralled.

At KNF Neuberger Inc., we specialize in providing high-performance vacuum pumps tailored to meet the demanding needs of diverse industries. Our vacuum pumps are designed with precision and reliability, offering optimal solutions for applications ranging from laboratory and medical environments to industrial and processing fields.
At Vacuubrand, we specialize in providing advanced vacuum technology solutions tailored for laboratory and industrial applications. We manufacture a comprehensive range of vacuum pumps, including oil-free diaphragm pumps, rotary vane pumps, and hybrid systems, all engineered for reliability, chemical resistance, and low maintenance.
Airtech is a leading manufacturer/supplier of various types of quality dry piston vacuum pressure pumps, rotary vane pumps (lubricated, dry), liquid ring vacuum pumps. We possess vast knowledge as a vacuum specialist. Serving medical, dental, food packaging and other industries. US warehousing.
At Welch Vacuum, we specialize in the design and manufacturing of high-quality vacuum pumps tailored to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. With a long history of innovation, we deliver reliable and efficient solutions for applications ranging from laboratory research to industrial processes.
More Vacuum Pump Manufacturers
Applications
Vacuum pumps are crucial across a wide range of industrial and commercial settings, serving as indispensable components in diverse applications. Their ability to create, maintain, and regulate a vacuum environment makes them vital in laboratories, medical facilities, dental clinics, and numerous manufacturing processes. These versatile machines are also utilized in specialized high-tech applications such as ion implantation, dry etching, atomic layer deposition, electron microscopy, radiotherapy, and radiosurgery, supporting innovation and precision across science and industry.
In laboratory environments, vacuum pumps are essential for maintaining contamination-free conditions. They are extensively used in sample preparation, filtration, rotary evaporation, freeze-drying, and aspiration, enabling researchers to perform sensitive experiments and analytical procedures with accuracy. Their ability to create low-pressure environments ensures the integrity and reproducibility of experimental results.
Within healthcare and medical settings, medical vacuum pumps provide the necessary suction for surgical and dental operations. They help maintain clear surgical fields, improve visibility for practitioners, and enhance patient safety by removing fluids and debris. Medical-grade vacuum systems are also integrated into central vacuum installations in hospitals, supporting a range of life-saving equipment, anesthesia systems, and respiratory care devices.
Industrial manufacturing processes benefit extensively from vacuum pump technology. Applications include vacuum forming and molding of plastics, degassing, packaging, material handling, and pick-and-place operations. In electronics and semiconductor production, vacuum pumps are indispensable for wafer fabrication, vacuum coating, and cleanroom management. Specialized applications extend to the production of eyeglass lenses, light bulbs, and vacuum tubes, where precise atmospheric control is non-negotiable.
Key industries relying on vacuum pump systems include:
- Laboratory and research
- Healthcare, medical, and dental
- Industrial and manufacturing
- Plastic molding and forming
- Food processing and packaging
- Semiconductor and microelectronics
- Vacuum coating and deposition
- Pharmaceutical and biotechnology
- Automotive and aerospace
Are you seeking a vacuum pump solution for a specific application or industry? Explore our directory of vacuum pump manufacturers to compare options and find the best system for your requirements.
The History of Vacuum Pumps
The development of vacuum pump technology has a rich history, marked by scientific ingenuity and technological progress. Early vacuum pumps were primarily created for scientific demonstrations and research, with initial models crafted from glass and sealed using liquid compounds. These first-generation pumps involved placing a large jar upside down on a surface with an outlet and using a manual pump to draw out the air, thus generating a partial vacuum.
The first practical vacuum pump is attributed to Otto Von Guericke, a Prussian engineer and physicist, who invented the air pump in 1650. Guericke’s device could achieve much lower pressures than earlier systems, paving the way for advanced vacuum research. His famous Magdeburg hemispheres experiment in 1654 dramatically illustrated vacuum power—demonstrating that even teams of horses could not separate two hemispheres joined by a vacuum. The 1660s saw further refinements by Irish scientist Robert Boyle and his collaborator Robert Hooke, who improved the air pump’s design and conducted foundational experiments on the properties of vacuums.
Interest in vacuum technology subsided until 1855, when Heinrich Geissler invented the mercury displacement pump, a breakthrough that enabled the development of the vacuum tube—a critical component in early electronics. In 1865, Hermann Sprengel’s invention of the Sprengel pump, which used mercury drops to capture and remove air, further advanced vacuum science. Later, innovators like Nikola Tesla integrated Sprengel pumps into devices requiring high vacuum levels, such as experimental light sources and electrical apparatuses.
These 19th-century vacuum pumps, while relatively simple and limited in capacity, laid the foundation for today’s high-performance, energy-efficient, and reliable vacuum pump systems. Modern vacuum pumps build upon this legacy, offering advanced features, automated controls, and robust materials to meet the demands of contemporary industries and research laboratories.
Design
Modern vacuum pump design focuses on performance, durability, and compatibility with demanding operational environments. Manufacturers construct vacuum pumps using robust, corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum alloys, or specialized polymers to ensure long service life and resistance to chemical attack. The selection of materials often depends on the process gases, required cleanliness, and specific industry regulations.
Key design considerations for vacuum pump systems include:
- Material compatibility: Choosing materials suited to the gases or liquids being pumped to avoid corrosion or contamination.
- Vacuum levels: Specifying both maximum and minimum achievable vacuum (ultimate pressure), tailored to the application’s needs—ranging from rough vacuum (low vacuum) to high vacuum and ultra-high vacuum.
- Flow rates: Determining required pumping speed (measured in liters per second or cubic feet per minute) to ensure efficient evacuation.
- Pump size and footprint: Selecting appropriate dimensions and mounting configurations for space-constrained installations or mobile setups.
- Pump speed: Factoring in variable speed drives or fixed speed options for process efficiency.
- Sealing and containment: Ensuring leak-tight operation through advanced gasket materials, O-rings, and chamber designs.
Manufacturers may also offer customized vacuum pump systems by integrating multiple pumps in series or parallel, incorporating specialized chambers, seals, control valves, and automation features to achieve precise vacuum levels and accommodate complex process requirements.
Wondering how to select the right vacuum pump design for your facility or application? Browse our listings or contact a manufacturer directly to discuss your project specifications and get expert recommendations.
Features
Vacuum pumps are engineered with a variety of features to optimize performance, reliability, and user control. At the core of every vacuum pump system are several critical components:
- Inlet port: The entry point for air or gas, connecting the pump to the process chamber or system via a sealed opening.
- Pumping mechanism: The internal method (e.g., rotary vane, diaphragm, piston, turbomolecular) that generates suction and expels gas or vapor from the chamber.
- Outlet/exhaust port: The exit path for evacuated gases, often routed through filters or condensers to capture contaminants and protect downstream equipment.
- Gaskets and seals: High-performance elastomers such as rubber, silicone, or fluoropolymers ensure leak-free operation, maintaining the integrity of the vacuum environment.
- Valves: Precision valves regulate gas flow, enable pressure control, and isolate different sections of the system for maintenance or process control.
- Gauges and sensors: Integrated pressure gauges, vacuum transducers, and digital sensors provide real-time monitoring and feedback, allowing for automated adjustments and process optimization.
- Control mechanisms: Advanced vacuum pumps may feature programmable logic controllers (PLCs), touchscreen interfaces, remote monitoring, and safety interlocks for enhanced usability and process automation.
These features collectively ensure that vacuum pumps deliver consistent, reliable performance in critical applications. From simple manual pumps to fully automated industrial vacuum systems, the right combination of features is essential for operational efficiency, safety, and process control.
Looking for a vacuum pump with specific features such as automated controls, low noise operation, or cleanroom compatibility? Search our manufacturer directory to find models that meet your unique requirements.
Types
Vacuum pump systems are available in numerous types, each tailored to distinct applications and performance needs. Yet, their fundamental principle remains the same: removing air or gas from an enclosed space and preventing its return. Understanding the different vacuum pump technologies helps users select the ideal solution for their industry or process.
Three primary vacuum generation methods define most pump types:
- Positive displacement pumps: Mechanically expand and contract a cavity to draw in and expel gases. Examples: rotary vane pumps, scroll pumps, piston pumps, diaphragm pumps, and liquid ring vacuum pumps. Best suited for low to medium vacuum applications, such as packaging, degassing, and laboratory work.
- Momentum transfer (kinetic) pumps: Use high-speed rotating or moving parts to impart momentum to gas molecules, directing them toward the exhaust. Examples: diffusion pumps, turbomolecular pumps. Preferred for creating high and ultra-high vacuum environments, common in semiconductor manufacturing, coating, and analytical instrumentation.
- Entrapment pumps: Capture and immobilize gas molecules on cold surfaces or via chemical reaction. Types include cryo pumps (using extremely cold arrays to condense gases) and ion pumps (embedding ions in metal surfaces by electric fields). Entrapment pumps are vital for achieving ultra-high vacuum, as needed in advanced physics research, mass spectrometry, and vacuum coating.
All vacuum pump systems can also be classified as wet or dry, based on whether they use liquid media during operation:
- Wet vacuum pumps: Employ liquids (such as oil or water) for sealing, lubrication, or cooling. Oil-sealed rotary vane and liquid ring pumps are examples. Wet pumps can attain lower ultimate pressures, but require careful maintenance to avoid contamination and ensure reliable operation. They are ideal for demanding industrial and laboratory applications that tolerate or require oil lubrication.
- Dry vacuum pumps: Operate without internal liquids, relying on dry seals and non-contacting mechanisms. Dry vacuum pumps reduce maintenance needs and eliminate oil contamination, making them well-suited for clean processes, such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, and food processing. However, they may have higher initial costs and are sometimes less effective at handling particulates or corrosive gases.
Some vacuum pumps combine features from different types for enhanced performance:
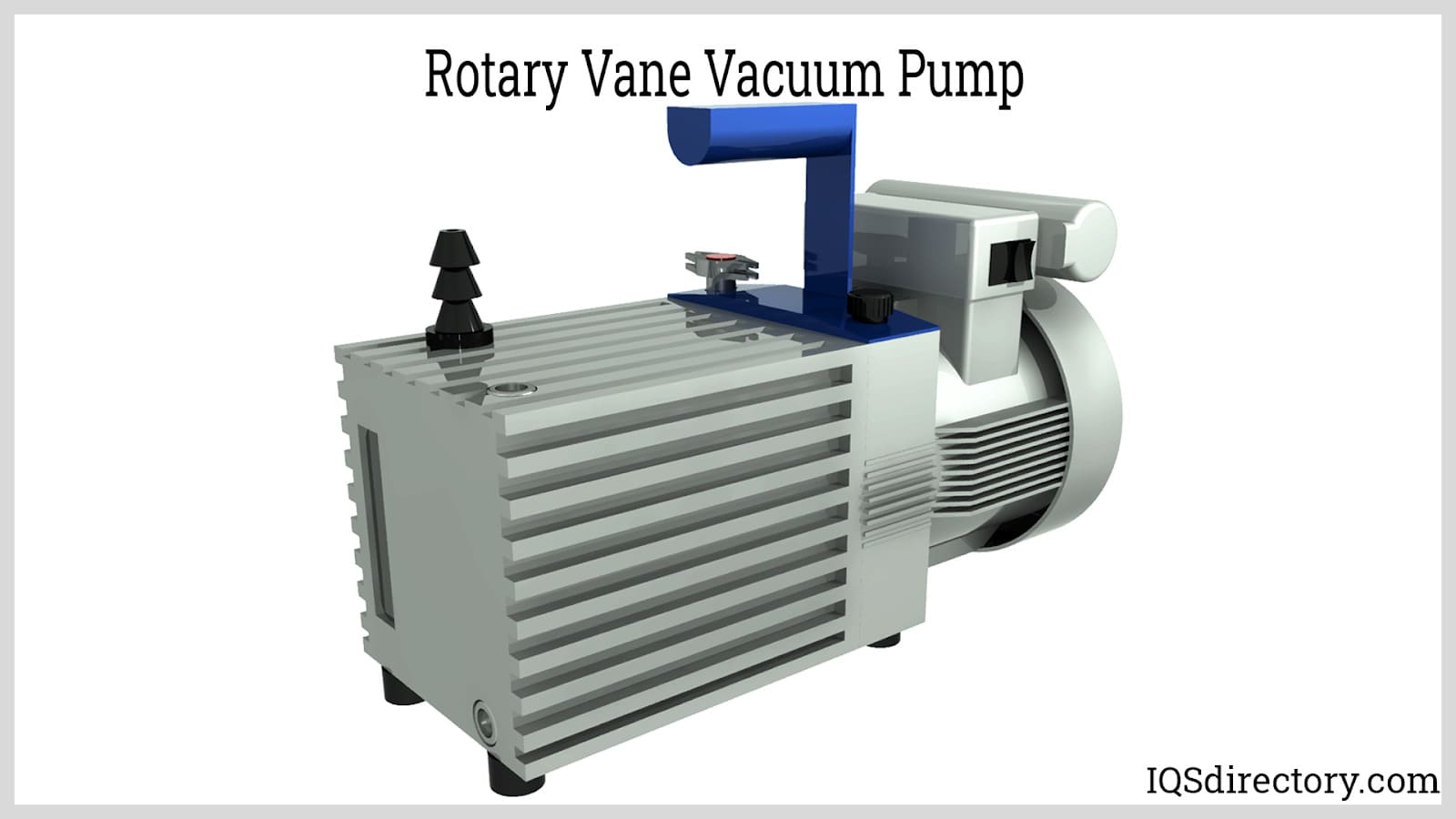
- Rotary vane vacuum pumps: Oil-sealed, air-cooled, and direct-drive, these pumps are valued for their compact design, energy efficiency, and ability to handle dry, clean, non-reactive gases. Popular in general laboratory, research, and industrial service.
- Screw air compressors (rotary-screw compressors): Use intermeshing helical screws to compress gas. Piston vacuum pumps, diaphragm pumps, and liquid ring pumps fall under the positive displacement category and are chosen for specific application advantages, such as pulsation-free flow or tolerance to wet gases.
- Piston vacuum pumps (rotary piston): Industrial vacuum pumps using reciprocating or rotating pistons, ideal for heavy-duty applications, vacuum metallurgy, and material handling.
- Diaphragm pumps: Use flexible membranes to move fluids, providing contamination-free and oil-free vacuum ideal for chemical processing, filtration, and environmental analysis.
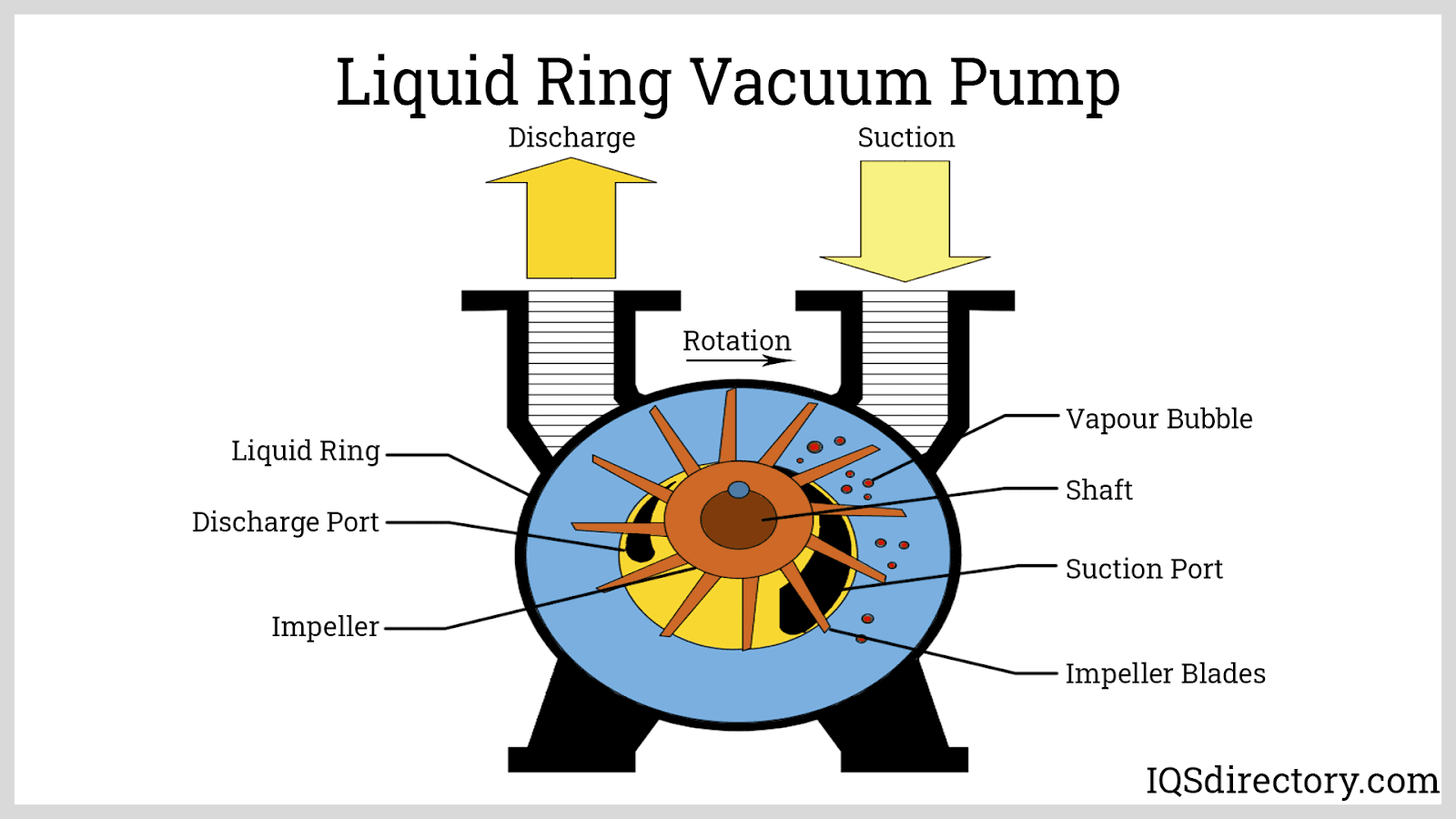
- Liquid ring vacuum pumps: Tolerate vapor and liquid ingestion, used for evacuating wet gases and handling condensable vapors or liquid-laden streams in chemical, power generation, and pulp and paper industries.
Specialized vacuum pump types include laboratory vacuum pumps, medical vacuum pumps, high vacuum pumps, and automotive vacuum pumps, each engineered for unique operational profiles and compliance with industry standards.
Trying to determine which vacuum pump type is right for your process? Consider these questions:
- What vacuum level (ultimate pressure) do you require?
- What is the required pumping speed or flow rate?
- Will you be handling corrosive, flammable, or particulate-laden gases?
- Do you need an oil-free (dry) or oil-sealed (wet) pump?
- What are your maintenance and lifecycle cost priorities?
Search our listings to compare vacuum pump types, technical specifications, and find manufacturers offering tailored solutions for your target application.
Advantages of Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum pumps deliver a host of performance and operational advantages, making them the preferred solution for creating controlled environments across a broad spectrum of industries. Key benefits include:
- Exceptional efficiency: Modern vacuum pumps rapidly evacuate gases, achieving target pressure levels quickly. This is critical for time-sensitive industrial processes and research experiments where delays can impact productivity and results.
- High reliability and durability: Engineered from robust, corrosion-resistant materials, vacuum pumps are designed for continuous operation in demanding settings, minimizing downtime and maximizing process uptime. Rigorous quality control and adherence to manufacturing standards ensure long service life.
- Superior vacuum performance: Vacuum pumps can achieve much lower pressures than alternative methods (such as venturi systems or manual pumping), enabling applications that require high vacuum or ultra-high vacuum—such as semiconductor fabrication, surface science, and advanced materials research.
- Precision control: Integrated sensors, gauges, and programmable controllers allow users to regulate and maintain exact vacuum levels for critical applications like freeze-drying, vacuum distillation, and vacuum packaging, ensuring consistent quality and safety.
- Versatility: A wide range of vacuum pump types and configurations are available, supporting everything from benchtop laboratory tasks to large-scale industrial processing lines. This versatility means users can select the ideal pump for their specific vacuum application, whether that involves handling aggressive chemicals, biological samples, or cleanroom environments.
- Energy efficiency: Newer vacuum pump designs incorporate variable speed drives, energy recovery systems, and advanced motor technology, helping facilities lower operational costs and reduce their environmental footprint.
- Minimal contamination risk: Dry (oil-free) vacuum pumps are available for applications where product purity is essential, such as pharmaceutical production, semiconductor processing, and food packaging.
In summary, vacuum pumps offer unmatched efficiency, reliability, and application flexibility. Their ability to deliver precise, controlled vacuum environments underpins progress and innovation in manufacturing, science, healthcare, and beyond.
Accessories
To maximize the performance and lifespan of vacuum pumps, a variety of vacuum pump accessories are available to support specific operating requirements and enhance overall system capability. Popular accessories include:
- Compressor kits: Convert a vacuum pump into a dual-purpose device, allowing for both vacuum generation and positive pressure output, expanding its utility across multiple applications.
- Vacuum gauges and sensors: Provide accurate, real-time measurement of pressure levels within the system, enabling operators to monitor and maintain optimal vacuum conditions for sensitive processes.
- Safety and relief valves: Protect the pump and system from over-pressurization or vacuum failure, ensuring safe operation and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Vacuum hoses and fittings: Flexible, chemical-resistant tubing and high-integrity connectors facilitate safe and leak-free transfer of gases between the pump and application chamber.
- Filters and condensers: Remove moisture, particulates, and chemical contaminants from exhaust gases, preserving pump performance and reducing maintenance.
- Power cord assemblies and electrical accessories: Ensure a reliable and compliant connection to power supplies, supporting safety and operational stability.
- Maintenance kits and spare parts: Include replacement seals, O-rings, oil, and gaskets, enabling regular upkeep and prompt repairs to reduce downtime.
Vacuum pump accessories are readily available from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), authorized distributors, online marketplaces, and industrial supply houses. For best results, always consult your vacuum pump manufacturer to verify compatibility and select high-quality, application-specific accessories.
Need help identifying the right accessories for your vacuum system? Contact a manufacturer or supplier to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal system configuration.
Proper Care for Vacuum Pumps
To ensure consistent performance and extend the service life of your vacuum pump, adopting a robust maintenance strategy is essential. Proper care begins with a thorough understanding of your pump’s design, operational limits, and common failure modes. Key maintenance tips include:
- Perform regular inspections for leaks, unusual noises, or performance drops—early detection prevents costly repairs and downtime.
- Follow the manufacturer’s schedule for oil changes, seal replacements, and filter cleaning or replacement, particularly for oil-sealed and wet vacuum pumps.
- Monitor lubricant and oil levels, ensuring the system is always adequately filled with clean, uncontaminated fluids.
- Keep the pump and surrounding area clean and free from dust or corrosive chemicals to avoid contamination and mechanical wear.
- Document maintenance activities and performance metrics to identify trends or recurring issues, supporting proactive decision-making.
- Train operators and maintenance personnel on proper startup, shutdown, and troubleshooting procedures to maximize safety and reliability.
For critical applications, consider partnering with your vacuum pump supplier for preventive maintenance contracts, remote monitoring, or technical support. Adhering to a regular maintenance plan reduces total cost of ownership and ensures uninterrupted, high-quality vacuum performance.
Have questions about vacuum pump maintenance or troubleshooting? Find expert support by contacting leading manufacturers in our directory.
Standards
Vacuum pump systems must adhere to rigorous industry standards to ensure safety, reliability, and consistent performance. These standards, developed by leading technical organizations, establish best practices for design, manufacturing, testing, and operation.
In the United States, several prominent agencies and industry groups contribute to the development of vacuum pump standards:
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME): Publishes codes and standards for rotary pumps, vacuum technology, and pressure systems (e.g., ASME B73.1 for rotary pumps).
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Sets global guidelines for vacuum pump performance, testing, and safety, including ISO 21360-1 and ISO 21360-2.
- American Vacuum Society (AVS): Promotes vacuum science and technology, providing resources and standards for research and industrial users.
- National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA): Offers standards for electrical safety and compatibility in vacuum pump systems.
Why are vacuum pump standards important?
- They ensure interchangeability and compatibility among different vacuum pump systems, simplifying integration and upgrades in complex facilities.
- They establish quality assurance criteria, so users can trust that pumps meet performance, efficiency, and safety requirements.
- They support regulatory compliance for industries with strict operational or environmental mandates, such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and cleanroom manufacturing.
- They foster innovation and continuous improvement by incorporating emerging best practices and technological advancements.
Adherence to recognized standards is a hallmark of leading vacuum pump manufacturers. It ensures customers receive products that are reliable, safe, and effective—backed by third-party validation and industry consensus.
Searching for vacuum pumps that meet specific industry standards or certifications? Filter our manufacturer listings by compliance criteria to streamline your procurement process.
Choosing the Proper Vacuum Pump Manufacturer
When investing in a new vacuum pump system, selecting the right manufacturer is a critical decision that impacts long-term reliability, serviceability, and total cost of ownership. To achieve the best results and maximize return on investment, follow these steps:
- Research multiple manufacturers using our comprehensive directory. Each supplier features a detailed business profile outlining their specialties, technical expertise, and product range.
- Access the manufacturer’s profile page to review their application focus, certifications, engineering capabilities, and customer testimonials.
- Contact manufacturers directly for technical information, product catalogs, and expert advice tailored to your industry or process needs.
- Utilize our patented website previewer to quickly compare companies and identify those best aligned with your requirements.
- Leverage our straightforward RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact multiple manufacturers simultaneously, simplifying your procurement workflow and accelerating decision-making.
Key factors to consider when choosing a vacuum pump manufacturer:
- Proven track record in your industry or application area
- Compliance with relevant standards (ASME, ISO, CE, etc.)
- Comprehensive product support, technical assistance, and spare parts availability
- Ability to provide customized or turnkey vacuum solutions
- Competitive pricing and warranty terms
Ready to find the ideal vacuum pump partner for your next project? Start your search now and connect with industry-leading manufacturers through our easy-to-use platform.
Looking for more insights? Try these search prompts to explore further:
- What are the best vacuum pumps for pharmaceutical manufacturing?
- How do I size a vacuum pump for laboratory filtration?
- Which vacuum pump types are oil-free and suitable for cleanroom use?
- What are the benefits of upgrading to a variable speed vacuum pump?
- How can I reduce energy consumption in my vacuum pump system?
- What maintenance schedule should I follow for a rotary vane vacuum pump?
For answers to these questions and more, navigate our expert resources or contact a manufacturer listed in our directory.
What are the main applications of vacuum pumps?
Vacuum pumps are used in laboratories, medical facilities, dental clinics, and various manufacturing processes. They also play a vital role in high-tech applications like ion implantation, dry etching, atomic layer deposition, electron microscopy, radiotherapy, and radiosurgery, supporting precision and innovation in science and industry.
How has vacuum pump technology evolved over time?
Vacuum pump technology originated with early glass models and manual air pumps. Otto Von Guericke invented the first practical air pump in 1650, and innovations by Robert Boyle, Heinrich Geissler, and Hermann Sprengel further advanced the field. Modern vacuum pumps are now high-performance, energy-efficient machines made with robust materials and advanced features.
What are key design considerations when selecting a vacuum pump?
Key design considerations include material compatibility with process gases, required vacuum levels, pumping speed or flow rates, pump size and installation footprint, sealing and containment systems, and options for customizing with features like automation, specialized chambers, or multiple pumps.
What are the main types of vacuum pumps?
Vacuum pumps are classified into positive displacement pumps, momentum transfer (kinetic) pumps, and entrapment pumps. Examples include rotary vane, scroll, piston, diaphragm, diffusion, turbomolecular, cryo, and ion pumps. Pumps can also be wet (using oil or water) or dry (oil-free), and specialized types are available for laboratories, medical, industrial, and specific industry needs.
What are the main advantages of using vacuum pumps?
Vacuum pumps offer exceptional efficiency, high reliability, superior vacuum performance, precise control, versatility, energy efficiency, and minimal contamination risk. These benefits make them ideal for critical applications in manufacturing, science, healthcare, and other industries requiring controlled vacuum environments.
What accessories are commonly used with vacuum pumps?
Common vacuum pump accessories include compressor kits, vacuum gauges and sensors, safety and relief valves, hoses and fittings, filters and condensers, power cord assemblies, and maintenance kits. These accessories enhance system capability and help ensure optimal performance and longevity.
How can I maintain my vacuum pump for best performance?
Regular maintenance includes inspecting for leaks and abnormal noise, following manufacturer schedules for oil changes and filter replacements, monitoring oil levels, keeping the pump clean, documenting maintenance, and providing thorough operator training. For critical use, consider preventive contracts or remote monitoring by the supplier.
What standards should vacuum pump systems comply with?
Vacuum pump systems should comply with standards set by organizations such as ASME, ISO, AVS, and NEMA. These standards ensure safety, compatibility, quality, and regulatory compliance for industries with rigorous operational requirements.
What are the main applications of vacuum pumps?
Vacuum pumps are essential in laboratories, medical facilities, dental clinics, and various manufacturing processes. They are used for maintaining contamination-free environments, supporting surgical procedures, vacuum forming and molding, packaging, semiconductor production, and specialized science and industry operations.
How has vacuum pump technology evolved throughout history?
Vacuum pump technology began with early scientific models in the 17th century, including Otto Von Guericke’s air pump. Major developments such as the mercury displacement pump by Heinrich Geissler and the Sprengel pump revolutionized the 19th century, laying the groundwork for today’s high-efficiency, reliable systems used in research and industry.
What factors should be considered when designing a vacuum pump system?
Important design considerations include material compatibility, achievable vacuum levels, required flow rates, pump size, speed, as well as sealing and containment aspects. Customization may involve integrating multiple pumps and advanced control features to meet unique application requirements.
What are the primary types of vacuum pumps available?
Major vacuum pump types include positive displacement pumps (like rotary vane and diaphragm pumps), momentum transfer pumps (such as diffusion and turbomolecular pumps), and entrapment pumps (including cryo and ion pumps). Pumps are also categorized as wet (oil or water lubricated) or dry (oil-free) for different process demands.
What are the key advantages of using vacuum pumps?
Vacuum pumps provide high efficiency, reliability, and precise control for maintaining vacuum conditions. They offer versatility for various industries, enhanced energy efficiency, minimal contamination risk (especially with dry pumps), and can help achieve demanding vacuum levels necessary for advanced scientific and industrial processes.
What accessories are recommended for vacuum pump systems?
Common accessories include compressor kits, vacuum gauges and sensors, safety and relief valves, hoses, fittings, filters, condensers, power cords, maintenance kits, and spare parts. These enhance performance, ensure safety, and extend equipment lifespan.
What maintenance practices are important for vacuum pump longevity?
Proper care includes regular inspections, following scheduled lubrication and part replacements, monitoring for leaks or performance drops, keeping the system clean, documenting maintenance, and training operators. Preventive maintenance contracts and technical support from manufacturers can improve reliability and reduce ownership costs.
What standards and certifications should vacuum pump systems comply with?
Vacuum pump systems should adhere to standards from organizations such as ASME, ISO, AVS, and NEMA. Compliance ensures safety, performance, quality assurance, and regulatory adherence, especially in industries with strict operational demands.
What are the main applications of vacuum pumps?
Vacuum pumps are used in laboratories, medical facilities, dental clinics, manufacturing processes, electronics production, and high-tech industries like ion implantation and radiotherapy. They enable creating, maintaining, and regulating vacuum environments essential for processes such as sample preparation, filtration, surgeries, packaging, and semiconductor fabrication.
How has vacuum pump technology evolved over time?
Vacuum pump technology began with scientific demonstrations in the 17th century, notably Otto Von Guericke’s air pump and the Magdeburg hemispheres experiment. In the 19th century, advancements by Heinrich Geissler and Hermann Sprengel led to more efficient pumps, paving the way for vacuum tubes and early electronics. Modern pumps now feature robust materials, automation, and precise controls for advanced industrial and scientific use.
What are the key features to look for in a vacuum pump?
Key vacuum pump features include an inlet port, specialized pumping mechanism, outlet/exhaust port, high-performance gaskets and seals, precision valves for pressure control, integrated gauges and sensors for monitoring, and advanced control mechanisms such as programmable logic controllers or touchscreen interfaces for automation and safety.
What are the main types of vacuum pumps available?
There are three main types of vacuum pumps: positive displacement pumps (e.g., rotary vane, diaphragm), momentum transfer/kinetic pumps (e.g., diffusion, turbomolecular), and entrapment pumps (e.g., cryo, ion pumps). Pumps are also classified as wet (using liquids for operation) or dry (oil-free). Specialized pump types exist for unique applications, such as medical, laboratory, or high vacuum uses.
What are the benefits of using modern vacuum pumps?
Modern vacuum pumps offer efficient evacuation, high reliability and durability, ability to achieve low pressures, precision control, versatility across many applications, energy efficiency, and minimal risk of contamination especially with dry (oil-free) designs, making them suitable for critical industries like pharmaceuticals and electronics.
What accessories are commonly used with vacuum pumps?
Common vacuum pump accessories include compressor kits, vacuum gauges and sensors, safety and relief valves, hoses and fittings, filters and condensers, power cord assemblies, and maintenance kits with spare parts. These accessories enhance performance, protect sensitive components, and support reliable operation.
How should vacuum pumps be maintained for optimal performance?
To maintain vacuum pumps, regularly inspect for leaks or performance changes, follow manufacturer schedules for oil and filter changes, monitor lubricant levels, keep equipment clean, document maintenance actions, and train staff in safe operation and troubleshooting. Preventive maintenance and expert support further ensure longevity and reliability.
Why are industry standards important for vacuum pump systems?
Industry standards ensure vacuum pump systems are safe, reliable, and compatible with other equipment. Standards from ASME, ISO, AVS, and NEMA cover aspects like design, performance, testing, and electrical safety, providing quality assurance and facilitating compliance with regulatory requirements.




 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services