Oilless pumps are used in contexts in which accidental exposure to oil could damage products or endanger people. Medical vacuum pumps are often oilless to minimize patient and instrument exposure to oil. In the fabrication of hi-tech electronics, oilless pumps may also be necessary to avoid contaminating sensitive instruments with small amounts of oil. Read More…
Busch Vacuum Solutions is a leading manufacturer of vacuum pumps, blowers, compressors, and customized systems using vacuum technology. With over 60 years of experience, Busch offers the largest selection of industrial vacuum and pressure technology available today to meet their customer’s operating and cost saving goals. Contact us today!
Founded in 1885, Becker is still family owned and a leader in innovation. From their innovative products & designs to their team of loyal, experienced & talented employees, you will find the solutions you are looking for at Becker. Becker’s vacuum pumps are of the highest quality and you are guaranteed to go home satisfied and continue to be satisfied in the many years to come.
Gast Manufacturing specializes in rotary vane, oilless, miniature, high-volume and dry vacuum pump products. We provide efficient, reliable vacuum pumps for a variety of applications. Our commitment to quality products, great service and environmentally friendly practices is unparralled.

At KNF Neuberger Inc., we specialize in providing high-performance vacuum pumps tailored to meet the demanding needs of diverse industries. Our vacuum pumps are designed with precision and reliability, offering optimal solutions for applications ranging from laboratory and medical environments to industrial and processing fields.
At Vacuubrand, we specialize in providing advanced vacuum technology solutions tailored for laboratory and industrial applications. We manufacture a comprehensive range of vacuum pumps, including oil-free diaphragm pumps, rotary vane pumps, and hybrid systems, all engineered for reliability, chemical resistance, and low maintenance.
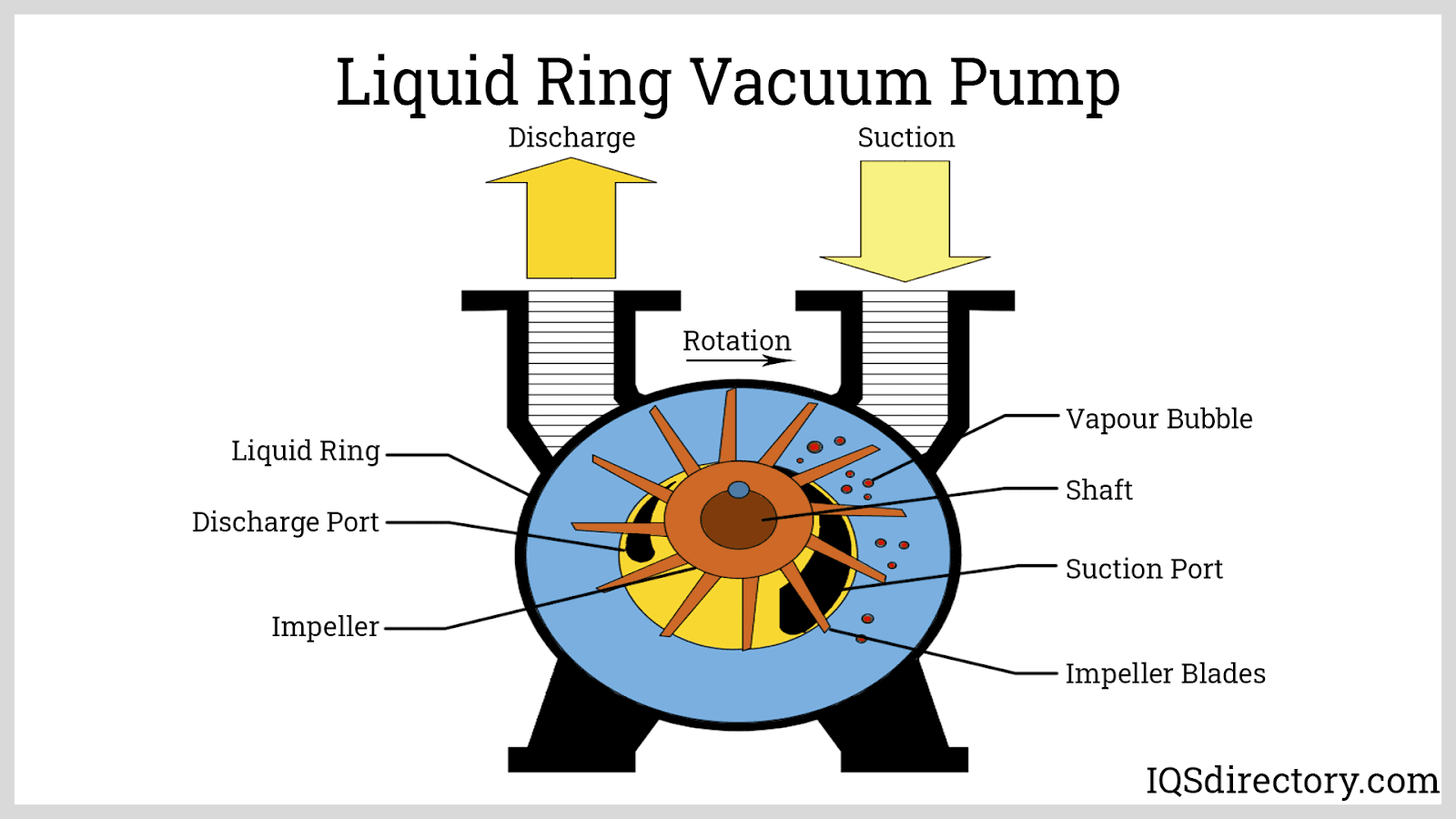
Airtech is a leading manufacturer/supplier of various types of quality dry piston vacuum pressure pumps, rotary vane pumps (lubricated, dry), liquid ring vacuum pumps. We possess vast knowledge as a vacuum specialist. Serving medical, dental, food packaging and other industries. US warehousing.
At Welch Vacuum, we specialize in the design and manufacturing of high-quality vacuum pumps tailored to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. With a long history of innovation, we deliver reliable and efficient solutions for applications ranging from laboratory research to industrial processes.
More Oilless Vacuum Pump Manufacturers
Industrial Applications, Selection, and Benefits of Oil-Less Dry Vacuum Pumps
In a wide range of industrial environments, vacuum pumps play a critical role in enabling essential processes such as dry etching, solvent recovery, material handling, vacuum distillation, petrochemical processing, food manufacturing, finishing, packaging, pharmaceutical production, and electronics fabrication. Among the different types of vacuum pumps available, oil-less dry vacuum pumps have emerged as a preferred solution for industries seeking clean, reliable, and cost-effective vacuum generation without the risks associated with lubricating oils.
What Is a Dry Vacuum Pump?
A dry vacuum pump—sometimes called an oil-free vacuum pump or oilless vacuum pump—is a positive displacement pump designed to operate without the use of oil or other liquid lubricants in the compression chamber. This key characteristic makes dry pumps highly attractive for applications where oil contamination is unacceptable, such as in semiconductor manufacturing, laboratory analysis, cleanroom environments, and food processing.
Comparing Dry and Wet Vacuum Pumps
When evaluating dry vacuum pumps vs. wet (oil-sealed) vacuum pumps, organizations must consider initial investment, operational costs, performance, and risk of contamination:
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership: Dry vacuum pumps are generally less expensive over their lifetime than wet pumps, thanks to reduced maintenance, fewer consumables, and lower disposal fees for hazardous waste.
- Contamination Risk: A dry vacuum pump failure typically poses a lower risk to product quality and system integrity than a wet pump failure, as there is no oil or liquid to contaminate the vacuum chamber or process gases. In sensitive processes, oil contamination can be catastrophic, damaging both equipment and end products.
- Sealing and Performance: While oil-sealed pumps can achieve tighter seals and higher ultimate vacuum levels, modern dry pumps offer robust performance for most industrial vacuum applications. However, their vacuum generation capacity may be slightly lower due to the absence of oil sealing.
Considering a Vacuum Pump Upgrade?
Are you deciding between an oil-sealed vacuum pump and a dry vacuum pump for your facility? Explore common use cases and compare the benefits to determine which solution aligns best with your operational needs and industry regulations.
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers for Dry Vacuum Pump Adoption
The development of dry vacuum pumps was largely motivated by increasing awareness of the environmental and health hazards posed by traditional vacuum pump oils. Historically, many vacuum pump oils contained polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), substances now recognized as toxic, carcinogenic, and persistent environmental pollutants.
As environmental regulations have tightened and industry standards have evolved, organizations have sought vacuum pump technologies that eliminate the use of hazardous oils. Dry vacuum pumps not only remove the risk of PCB and hydrocarbon contamination but also simplify compliance with EPA, OSHA, and international clean manufacturing guidelines.
Need to Meet Strict Environmental or Product Purity Regulations?
If your industry demands oil-free processes—such as semiconductor fabrication, pharmaceutical manufacturing, or food and beverage production—a dry vacuum pump is often the only viable choice. Learn how to choose the right dry pump for regulated environments.
Maintenance and Reliability Advantages of Oil-Free Vacuum Pumps
One of the most significant advantages of oil-free vacuum technology is simplified maintenance. Dry pumps eliminate the need for regular oil changes, filter replacements, and disposal of contaminated lubricants. This not only reduces ongoing operational costs but also minimizes downtime and labor requirements.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: No need for routine oil or fluid checks, oil changes, or filter replacements.
- Minimized Waste Management: No hazardous oil or fluid disposal necessary, reducing environmental impact and compliance costs.
- Improved Uptime: Fewer moving parts and less routine maintenance mean higher system reliability and less unscheduled downtime.
How Does a Dry Vacuum Pump Work?
Oilless vacuum pumps are typically constructed from heavy-duty stainless steel for maximum strength and contamination resistance. Depending on the specific application and work environment, dry pumps may be equipped with:
- Vibration isolators to reduce operational noise and mechanical stress.
- Silencers for environments where low noise is critical.
- Cooling water jackets to manage the high internal temperatures resulting from the lack of oil as a coolant and sealant.
Every oilless vacuum pump is classified as a positive displacement pump—meaning it moves a fixed volume of gas per operating cycle. The three primary subcategories of dry vacuum pumps are rotary lobe, helical screw, and claw pumps. Each utilizes a unique rotor design to trap and compress gases efficiently.
Types of Dry Vacuum Pumps: Rotary Lobe, Helical Screw, and Claw
- Rotary Lobe Dry Vacuum Pumps: These pumps operate using two counter-rotating lobes that trap and compress gases, then convey them out of the pump chamber. Rotary lobe pumps are similar in some aspects to rotary vane pumps but do not require oil for sealing, reducing maintenance and contamination risk.
- Helical Screw Dry Vacuum Pumps: Employing two intermeshing screw-like rotors, these pumps trap process gases between the rotor threads, move them axially, and discharge them at the exhaust. Helical screw pumps are known for their high efficiency and ability to handle particulate-laden or condensable gases.
- Claw Dry Vacuum Pumps: Using two claw-shaped rotors, these pumps compress gases without contact between the rotors and the pump housing. Claw pumps offer high reliability, low energy consumption, and are particularly suited for continuous operation in demanding industrial environments.
Curious About Which Dry Pump Design Is Best for You?
Wondering whether a rotary lobe, helical screw, or claw dry vacuum pump is right for your process? Compare design advantages and explore typical applications for each technology below.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases for Dry Vacuum Pumps
Dry vacuum pumps are engineered for a diverse array of industrial and scientific processes where oil-free vacuum generation is essential. Common use cases include:
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Dry pumps are critical for wafer processing, photolithography, ion implantation, and plasma etching, where even trace oil contamination can cause defects and reduce yield.
- Pharmaceutical Production: Used in tablet coating, freeze drying (lyophilization), vacuum distillation, and solvent recovery, where product purity and compliance with GMP standards are mandatory.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Supporting applications like freeze drying, vacuum packaging, and aroma recovery, where oil-free operation ensures product safety and taste integrity.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industries: Ideal for degassing, distillation, and solvent recovery processes, dry pumps handle corrosive or reactive gases without the risk of oil backstreaming or fluid contamination.
- Laboratory and Analytical Instruments: Oil-less vacuum pumps support mass spectrometry, electron microscopy, glove boxes, and other precision instruments requiring clean, stable vacuum environments.
- Industrial Coating and Finishing: Used in vacuum metallization, sputtering, and plasma-enhanced deposition, where oil contamination would compromise coating adhesion and appearance.
- Medical and Dental Equipment: Dry pumps power suction devices, sterilization systems, and vacuum ovens, maintaining a sterile and safe environment.
Have a Specific Application in Mind?
Looking for the ideal oil-free vacuum pump for your application? See how to select the best dry pump for your process requirements.
Key Benefits of Oil-Less Dry Vacuum Pumps
Choosing a dry vacuum pump offers distinct advantages for industrial, laboratory, and research environments. Key benefits include:
- Clean, Oil-Free Operation: Zero risk of process contamination from oil vapors or backstreaming, ensuring product integrity and compliance with strict industry standards.
- Lower Maintenance and Operating Costs: Significantly reduced need for oil changes, consumables, and waste disposal, leading to lower total cost of ownership.
- Environmental Safety: No hazardous oil waste generation, supporting sustainability initiatives and helping facilities meet environmental regulations.
- High Reliability and Long Service Life: Robust, wear-resistant designs minimize downtime and maximize productivity in continuous-duty settings.
- Energy Efficiency: Many modern dry pumps offer variable speed drives and advanced controls, optimizing energy use for lower utility costs.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Essential for industries governed by FDA, GMP, ISO, and environmental regulations that prohibit oil-based contamination.
Seeking Long-Term Value and Sustainability?
Discover how oil-free vacuum technology can help your organization achieve operational efficiency, sustainability goals, and regulatory compliance. Compare lifecycle costs and environmental impact of dry vs. wet vacuum pumps.
How to Choose the Right Dry Vacuum Pump: Decision Factors
When selecting a dry vacuum pump for your application, consider the following factors to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and value:
- Vacuum Level Requirements: Determine the ultimate vacuum (pressure) and pumping speed needed for your process. Some dry pumps are tailored for high vacuum (HV) or low/rough vacuum (LV) applications.
- Process Gas Compatibility: Assess the chemical composition of process gases or vapors, including corrosive, condensable, or particulate-laden streams. Choose pump materials and designs suited for the intended environment.
- Throughput and Duty Cycle: Evaluate the required gas flow rate, process duration, and continuous vs. batch operation. Some pump types are better suited for 24/7 operation or high-throughput processes.
- Noise, Heat, and Footprint Constraints: Consider facility requirements for low noise operation, heat dissipation, and available installation space.
- Energy Consumption: Assess the energy efficiency of competing pump models, particularly for large-scale or long-duration processes.
- Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs: Factor in not only the initial purchase price, but also service intervals, part replacement costs, and expected service life.
- Compliance and Certification: Ensure the pump meets all relevant safety, environmental, and product purity standards for your industry and locale.
Ready to Compare Dry Vacuum Pump Models?
Start your search by identifying your process requirements, then request quotes or compare manufacturers for detailed specifications and support.
Frequently Asked Questions About Oil-Less Dry Vacuum Pumps
- What is the difference between an oil-sealed and oil-free vacuum pump?
Oil-sealed pumps use oil to lubricate, cool, and seal internal components, allowing for higher vacuum levels but introducing contamination risk. Oil-free (dry) pumps use air-tight mechanical designs to eliminate oil, prioritizing clean operation. - Are dry vacuum pumps suitable for corrosive gases?
Many dry pumps are available in corrosion-resistant configurations (e.g., stainless steel, PTFE coatings) suitable for aggressive process gases. Always check compatibility before purchase. - How often does a dry vacuum pump need maintenance?
Dry pumps typically require less frequent maintenance than oil-sealed models. Service intervals depend on the pump type and process conditions but are generally longer, reducing downtime and cost. - Can dry vacuum pumps achieve the same vacuum levels as wet pumps?
While some oil-sealed pumps can reach deeper vacuums, most modern dry pumps deliver sufficient performance for the vast majority of industrial and laboratory uses. - What industries use oil-less dry vacuum pumps most?
Common sectors include semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food processing, chemicals, energy, and environmental engineering.
Still Have Questions?
Not sure which vacuum pump technology is right for your process? Contact a specialist or browse leading vacuum pump manufacturers for expert advice and technical support.
Conclusion: The Future of Industrial and Scientific Vacuum Technology Is Oil-Free
As industries worldwide strive for higher product quality, greater process efficiency, and improved sustainability, the adoption of oil-less dry vacuum pumps will continue to accelerate. With their clean, reliable performance, reduced operating costs, and compliance with stringent environmental and product purity standards, dry pumps are the technology of choice for today's most demanding vacuum applications.
Whether you are upgrading legacy vacuum systems, planning a new facility, or seeking to optimize your production line, investing in oil-free vacuum pump solutions offers measurable benefits in operational reliability, cost savings, and regulatory compliance. Explore your options, compare models and suppliers, and take the next step toward a cleaner, more efficient vacuum process.





 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services